Table of Contents
According to the EIA, Americans can expect to pay more than ever for heating their homes this winter thanks to rising fuel costs across the globe.
So, if you use a fireplace as a major source of warmth during the chilly season, now is a good time to upgrade to a more energy-efficient model.
Not only will this save you money, but it’s also an environmentally friendly choice that helps you cut down on carbon emissions. Keep reading to discover whether a wood, electric, or gas fireplace is the most energy efficient.
What Does Energy Efficient Mean?
Energy efficiency means eliminating energy waste, i.e. using less energy to perform a task. For instance, LED lights can produce the same amount of light as incandescent bulbs, but they use 75% less electricity in the process.
For fireplaces, three things come into play regarding efficiency, namely:
- The BTUs used for gas fireplaces
- The wattage of electric fireplaces
- Amount of BTUs generate i.e. heat produced
- How much space they can heat
Energy efficiency has several important benefits, such as:
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- Decreasing demand for energy imports
- Lowering household costs
Renewable energy is the best way to enjoy the above benefits, but it makes sense to choose an energy-efficient model every time you upgrade or install a home appliance, including your fireplace.
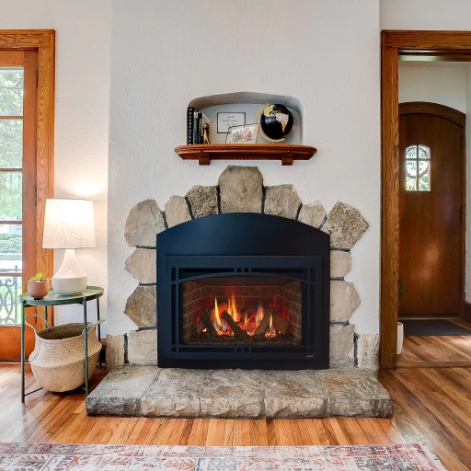
Wood Fireplaces and Energy Efficiency
A wood fireplace adds endless charm to classic living spaces. They create a wonderful ambiance and are one of the most reliable ways to heat a space.
Many off-grid residences rely on wood fireplaces as a source of warmth.
Although wood fireplaces require some maintenance, and produce soot, wood is an abundant and affordable source of fuel, depending on where you live. When harvested responsibly, wood is an eco-friendly and sustainable source of energy.
Always buy wood that originates from sustainable plantations and logging operations, and you can also opt for waste wood like recycled pellets, debris, and deadfall.
Traditional fireplaces are only around 10% efficient, but modern wood-burning fireplace designs achieve efficiency ratings of around 75%.
Whichever type of fireplace you have, there are a few ways to increase its efficiency:
- Burn seasoned firewood
- Open the damper as wide as possible
- Clean your chimney once a year
- Install tempered glass doors on the face of your fireplace
- Add a fireplace insert with a circulating fan
- Add insulation
- Install a fan heat exchanger
Investing in a new fireplace is still the best low-maintenance, high-efficiency choice for homeowners.
Electric Fireplace Efficiency
Electric fireplaces are readily available and easy to run, provided you’re connected to the grid. It’s easy to set them up, they don’t require a chimney, and they don’t create any harmful emissions.
They’re an excellent choice in warmer climates with mild winters, or for heating small spaces. They also boast slick modern designs that look great in any room.
Choosing an electric fireplace means you’re relying on fossil fuels to heat your home, unless you already have solar panels installed. This isn’t necessarily a bad thing, though.
Electricity is an inefficient way to produce heat. You need a lot of electricity to produce even a little heat, and you’ll need to spend a lot more money keeping your interiors warm in the winter.
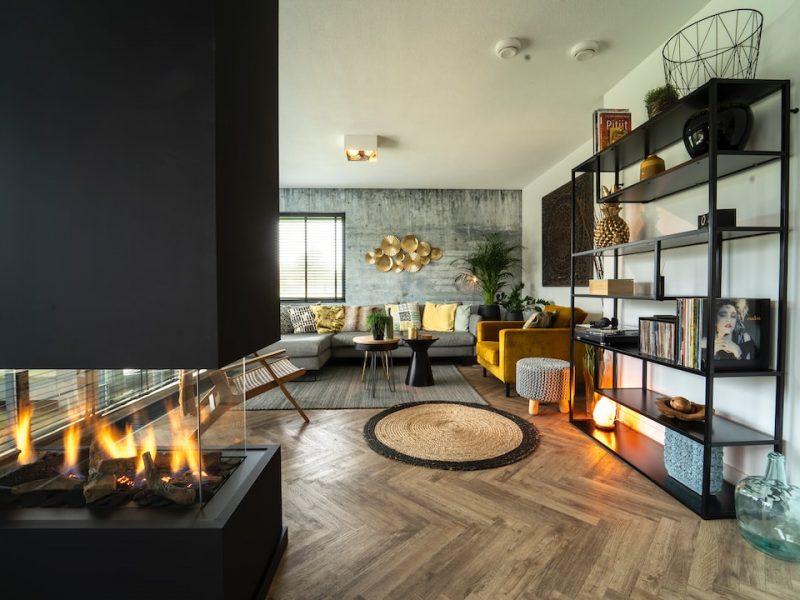
Are Gas Fireplaces Energy Efficient?
Gas fireplaces provide convenient, quick heating, and they’re easy to use. Natural gas is an abundant source of energy that burns clean and leaves very little residue.
It’s also an affordable source of fuel that delivers a lot of bang for your buck when combined with a modern, fuel-efficient fireplace design.
Gas fireplace efficiency depends on the type of fireplace you choose. The three main types of gas fireplaces available are vent-free, direct vent, and B-vent fireplaces.
Vent-Free Fireplaces
Vent-free gas fireplaces have no air vents on the outside, so all the heat they generate stays inside your home. Thanks to this, they boast efficiency ratings of around 99.9%.
Due to the absence of an exterior outlet, you must always have adequate air available to ensure combustion and adequate ventilation.
Not all states allow ventless fireplaces, so make sure you know your local regulations before you buy one.
Direct Vent Fireplaces
Vented gas fireplaces are an effective source of supplemental heat. They have sealed glass fronts and a two-wall vent system.
You don’t lose any air from your home thanks to the glass doors, but the heat still circulates inside. Thanks to this, direct vent fireplaces are an efficient way to heat our home, with efficiency ratings of between 50 and 80%.
B-Vent Fireplaces
B-vent gas fireplaces are open-fronted traditional fireplaces that you can control easily using a dial. They’re naturally drafting, and vertical vented
They are highly ornamental but extremely inefficient. They rarely achieve efficiency levels above 30%.
You can add an outside air kit or glass front to limit the amount of air drawn out of your room, and increase the efficiency of a B-vent gas fireplace. Most homeowners choose these fireplaces for their aesthetic value.
Upgrade Your Home Responsibly
Nowadays, homeowners need to consider every avenue when it comes to creating a more eco-friendly home.
The fireplace you choose should reflect your awareness of the current challenges faced by fuel industries, as well as the imminent threat of global warming.
To make the best decision for your family, ask an energy expert for guidance, or speak to a local fireplace installer for expert advice. We can help you choose the most energy-efficient fireplace for your needs, get in touch today.
Latest Articles

Why Is My Garage Door Opener Opening Both Doors?
Table of Contents1 Understanding Garage Door Openers2 Common Issues with Garage Door Openers3 Why Is My Garage Door Opener Opening Both Doors?4 How to Troubleshoot

Is It Normal For Sparks To Come Out Of Chimney?
Table of Contents1 What Are Sparks in a Chimney?2 What Are the Dangers of Sparks in a Chimney?3 How to Prevent Sparks from Coming Out

How Garage Doors Work
Table of Contents1 Types of Garage Doors2 Components of a Garage Door3 How a Garage Door Works4 Safety Features of Garage Doors5 Maintenance and Troubleshooting