Manufacturer Products
- Advanced Architectural Grilleworks
- Amantii Fireplaces
- American Fyre Designs
- Ashley Hearth Products
- Blaze King
- Breeo Firepits
- Buck Stove Fireplaces
- David Kimberly Door Company
- DaVinci Custom Fireplaces
- Dimplex
- Drolet
- DuraVent
- Ecosmart Fire
- Eiklor Flames
- Element4
- Empire Comfort Systems
- Enervex
- Englander Stove
- Enviro Fireplaces
- European Home
- EverWarm Gas Logs
- Fire Garden
- Firegear Outdoors
- FireMagic
- Fireplace Xtrordinair
- FireRock Building Materials
- Fire Sense
- Flamerite Fires
- Flare Fireplaces
- Focus Fireplaces
- Forshaw Mantels
- Grand Canyon Gas Logs
- Harman Stoves
- Hearth & Home Technologies
- Heat & Glo
- HeatFast
- Heatilator
- Heatmaster Fireplaces
- Holly & Martin Fireplaces
- HPC Fire
- Instone
- IntelliFire Ignition System
- JC Bordelet
- Jotul
- Kingsman Fireplaces
- Leenders
- Lexington Hearth Mantels
- Litedeer Homes
- Lopi Stoves
- Malm Fireplaces
- Modern Flames Fireplaces
- Monessen Fireplaces
- Montigo Fireplaces
- Napoleon Fireplaces
- NetZero Fire
- Opti-Myst
- Ortal Fireplaces
- Osburn Fireplaces
- Outdoor Greatroom Company
- Outdoor Lifestyles Fireplaces
- Pearl Mantels
- Peterson Log Sets
- Planika USA
- Quadra-Fire
- Regency Fireplace Products
- Remii Fireplaces
- Renaissance Cooking Systems
- Sierra Flame Fireplaces
- SimpliFire
- SÓLAS Contemporary Fire
- Spartherm
- Stellar Fireplaces
- Stoll Industries
- Stuv America
- Superior Fireplaces
- Swiss Fire Cube
- The Bio Flame
- Travis Industries
- US Stove
- Valcourt
- Valor Fireplaces
- Ventis Fireplaces
- Vermont Castings
- Vogelzang Products
- White Mountain Hearth
- Advanced Architectural Grilleworks
- Amantii Fireplaces
- American Fyre Designs
- Ashley Hearth Products
- Blaze King
- Breeo Firepits
- Buck Stove Fireplaces
- David Kimberly Door Company
- DaVinci Custom Fireplaces
- Dimplex
- Drolet
- DuraVent
- Ecosmart Fire
- Eiklor Flames
- Element4
- Empire Comfort Systems
- Enervex
- Englander Stove
- Enviro Fireplaces
- European Home
- EverWarm Gas Logs
- Fire Garden
- Firegear Outdoors
- FireMagic
- Fireplace Xtrordinair
- FireRock Building Materials
- Fire Sense
- Flamerite Fires
- Flare Fireplaces
- Focus Fireplaces
- Forshaw Mantels
- Grand Canyon Gas Logs
- Harman Stoves
- Hearth & Home Technologies
- Heat & Glo
- HeatFast
- Heatilator
- Heatmaster Fireplaces
- Holly & Martin Fireplaces
- HPC Fire
- Instone
- IntelliFire Ignition System
- JC Bordelet
- Jotul
- Kingsman Fireplaces
- Leenders
- Lexington Hearth Mantels
- Litedeer Homes
- Lopi Stoves
- Malm Fireplaces
- Modern Flames Fireplaces
- Monessen Fireplaces
- Montigo Fireplaces
- Napoleon Fireplaces
- NetZero Fire
- Opti-Myst
- Ortal Fireplaces
- Osburn Fireplaces
- Outdoor Greatroom Company
- Outdoor Lifestyles Fireplaces
- Pearl Mantels
- Peterson Log Sets
- Planika USA
- Quadra-Fire
- Regency Fireplace Products
- Remii Fireplaces
- Renaissance Cooking Systems
- Sierra Flame Fireplaces
- SimpliFire
- SÓLAS Contemporary Fire
- Spartherm
- Stellar Fireplaces
- Stoll Industries
- Stuv America
- Superior Fireplaces
- Swiss Fire Cube
- The Bio Flame
- Travis Industries
- US Stove
- Valcourt
- Valor Fireplaces
- Ventis Fireplaces
- Vermont Castings
- Vogelzang Products
- White Mountain Hearth
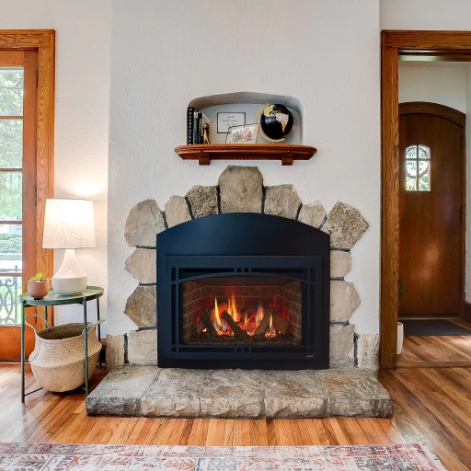
Stellar Fireplaces
History of the Company

Stellar Fireplaces, part of Heat & Glo, has revolutionized the fireplace industry since its inception.
The company’s journey began with a vision to transform traditional fireplaces into extraordinary experiences.
Pioneers in fireplace design and engineering founded Stellar, driven by a passion for innovation and excellence.
From the outset, Stellar Fireplaces focused on pushing the boundaries of what fireplaces could be.
Their commitment to advanced engineering and cutting-edge designs set them apart.
The company has continuously introduced innovative features and technologies, ensuring their fireplaces not only provide warmth but also enhance the aesthetic appeal of any space.
Stellar Fireplaces offers a wide range of customization options, allowing customers to tailor their fireplaces to fit their unique style and space requirements.
The use of commercial-grade components and stainless steel chassis ensures durability and superior performance.
Their frameless designs and advanced burner technologies create stunning visual impacts, making their fireplaces a focal point in any room.
Throughout its history, Stellar Fireplaces has maintained a dedication to quality and customer satisfaction.
Their team of experts works closely with clients from the initial design phase through to installation, ensuring a seamless experience and a final product that exceeds expectations.
Today, Stellar Fireplaces continues to lead the industry with its innovative designs and commitment to excellence, transforming living spaces with the timeless allure of fire.
Mission and Values
Stellar Fireplaces aims to redefine the fireplace experience.
Their mission focuses on creating exceptional spaces and unforgettable moments.
Stellar Fireplaces doesn’t just build fireplaces; they craft experiences that elevate the ambiance of any space.
Innovation stands at the core of Stellar Fireplaces.
They push boundaries and challenge the status quo, always seeking new ways to enhance the fireplace experience.
Their commitment to advanced engineering and cutting-edge designs ensures that every fireplace they create is a masterpiece of form and function.
Excellence is a way of life at Stellar Fireplaces.
They strive for perfection in every detail, using only the highest quality materials and components.
Their fireplaces feature commercial-grade parts and stainless steel chassis, ensuring durability and superior performance.
Customer-centricity guides every decision at Stellar Fireplaces.
They work closely with clients to bring their visions to life, offering unparalleled customization options.
From the initial design phase to installation, Stellar’s dedicated project managers ensure a seamless and satisfying experience.
Collaboration is another key value.
Stellar Fireplaces views clients as partners, working together to create defining experiences.
They provide personalized project management, ensuring proactive communication and meticulous attention to detail at every stage.
Quality underpins everything Stellar Fireplaces does.
They ensure the highest standards in design and engineering, guaranteeing that their fireplaces not only look stunning but also perform flawlessly.
Stellar Fireplaces’ mission and values reflect their commitment to transforming spaces with innovative, high-quality, and customizable fireplaces, always putting the customer first.
Overview of Products
Stellar Fireplaces offers a range of high-quality, customizable gas fireplaces designed to enhance any space.
Their product lineup includes the Enlight Collection, which features six distinct configurations: Single-Sided, Double-Sided, Pier, Corner, Bay, and Island.
Each design brings unique aesthetics and functionality, making them suitable for various indoor and outdoor settings.
The Enlight Single-Sided Gas Fireplace boasts the largest flames in its category, encased in crystal-clear glass without any corner posts, ensuring an uninterrupted view.
The Double-Sided Gas Fireplace creates a dynamic look by providing dramatic views of the flames from two sides, perfect for connecting different spaces while maintaining their distinct characters.
The Pier Gas Fireplace is ideal for open-concept designs, offering a three-sided view of the flames.
For those looking to add a stylish touch to their interior layout, the Corner Gas Fireplace can be placed on either the left or right side, available in multiple lengths and heights.
The Bay Gas Fireplace promotes gathering and relaxation, with vivid flames that add comfort without generating extra heat.
The Island Gas Fireplace stands out as a central piece, viewable from all sides, making it a focal point in any room.
In addition to the pre-configured designs, Stellar Fireplaces also allows for complete customization.
Customers can create their gas fireplaces in any shape, size, and location, incorporating bold flames, custom burners, and dramatic lighting options to suit their vision.
This flexibility ensures that every Stellar fireplace is a unique addition, perfectly tailored to the user’s style and space requirements.
Stellar Fireplaces emphasizes advanced technology and superior performance, ensuring that each product delivers maximum safety, efficiency, and comfort.
Their fireplaces feature UL-certified components, SafeSurface double-pane glass, and various venting options to meet the highest standards of durability and design flexibility.
Manufacturing Process
Stellar Fireplaces employs a meticulous and innovative manufacturing process to create their high-quality fireplaces.
The process begins with a detailed design phase, where engineers and designers collaborate to create blueprints and 3D models using advanced software.
As a result, every fireplace meets exact specifications and standards.
Once the design is finalized, the production phase begins with the selection of high-grade materials.
Stellar uses commercial-grade stainless steel for the chassis and advanced burner components.
These materials are chosen for their durability and resistance to high temperatures, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the fireplaces.
In the manufacturing facility, skilled craftsmen cut and shape the stainless steel using state-of-the-art machinery.
This includes laser cutting and CNC machining to achieve precise dimensions and clean finishes.
The components are then assembled, with special attention to the integration of the burners and other functional parts.
The fireplaces undergo rigorous quality control checks throughout the manufacturing process.
This includes testing the burners to ensure optimal flame presentation and performance.
The double-pane SafeSurface glass, used in many models, is also tested for safety and durability, ensuring it remains cool to the touch and meets UL certification standards.
Hand-finishing techniques are employed to add aesthetic details, such as custom media options and programmable LED lighting.
Each fireplace is customizable, allowing clients to tailor the design to their specific needs and preferences.
The final step involves a thorough inspection before packaging and shipping.
This ensures that every Stellar fireplace upholds the company’s commitment to quality and excellence, ready to transform any living space with unparalleled style and functionality.
Stellar Fireplaces combines cutting-edge technology with artisanal craftsmanship to produce fireplaces that are both beautiful and highly functional.
Advantages of Stellar Fireplaces
Stellar Fireplaces offers numerous advantages that set them apart in the industry.
Their fireplaces combine innovative design and cutting-edge technology to deliver superior performance and efficiency.
Stellar Fireplaces use high-quality materials, ensuring durability and long-lasting use.
Each fireplace boasts an elegant and modern aesthetic, seamlessly blending with various interior styles.
One of the key advantages is the energy efficiency of Stellar Fireplaces.
Their advanced technology maximizes heat output while minimizing fuel consumption, reducing energy costs for homeowners.
The fireplaces are designed to provide consistent and reliable heat, making any living space comfortable and cozy.
Safety is a top priority for Stellar Fireplaces.
They incorporate multiple safety features, including automatic shut-off systems and temperature controls, to ensure safe operation.
This makes them a reliable choice for families and homes.
Stellar Fireplaces are also easy to use and maintain.
Their user-friendly controls allow for simple operation, and the sleek designs make cleaning and maintenance hassle-free.
The company provides excellent customer support, ensuring that any issues are promptly addressed.
Customization is another significant advantage.
Stellar Fireplaces offer a range of styles, finishes, and sizes to fit any space and meet specific preferences.
Whether you need a compact fireplace for a small room or a grand statement piece, Stellar Fireplaces has options to suit your needs.
Finally, Stellar Fireplaces are environmentally friendly.
They use sustainable materials and technologies that reduce emissions and promote a cleaner environment.
This commitment to sustainability makes them a responsible choice for eco-conscious consumers.
In summary, Stellar Fireplaces provide energy efficiency, safety, ease of use, customization, and environmental benefits, making them a top choice for modern homes.
Considerations for Buyers
When considering a purchase from Stellar Fireplaces, evaluate key factors to ensure the best choice for your home.
First, assess the space for installation.
Measure accurately to determine the appropriate size and model that fits seamlessly without overwhelming the room.
Next, consider the fuel type that suits your lifestyle.
Stellar Fireplaces offer gas, electric, and wood-burning models.
Gas provides convenience and efficiency.
Electric offers easy installation and versatility.
Wood-burning creates a traditional ambiance but requires more upkeep.
Evaluate the heat output and efficiency.
Look for models with high energy efficiency ratings to save on utility bills.
Stellar Fireplaces maximize heat output while minimizing fuel consumption.
This ensures effective heating.
Consider the design and style of the fireplace.
Stellar Fireplaces offer options from modern to classic.
Choose a design that complements your home’s decor and enhances its appeal.
Safety features are crucial.
Stellar Fireplaces incorporate safety mechanisms like automatic shut-off systems and temperature controls.
Ensure these features meet your standards for peace of mind.
Budget is important.
Determine your price range and explore models that fit within it.
Stellar Fireplaces offer options across various price points.
This ensures you find a model that meets your needs and budget.
Think about installation and maintenance.
Professional installation ensures safety and optimal performance.
Stellar Fireplaces are designed for easy maintenance.
Regular cleaning and servicing will prolong their lifespan.
By considering space, fuel type, heat output, design, safety features, budget, and maintenance, you can confidently choose the perfect Stellar Fireplace for your home.
Frequently Asked Questions
Types of Fireplaces
Q: What types of fireplaces are available?
A: Stellar Fireplaces offers various types of fireplaces, including gas, wood-burning, electric, and pellet stoves, each with unique features and benefits.
Q: Can I convert a wood-burning fireplace to a gas fireplace?
A: Yes, you can convert a wood-burning fireplace to a gas fireplace with the help of a professional installer.
Q: What are the benefits of using a pellet stove?
A: Pellet stoves are known for their efficiency, low emissions, and ease of use. They are a popular choice for supplemental heating.
Energy Efficiency
Q: Are gas fireplaces more energy-efficient than wood-burning ones?
A: Yes, gas fireplaces are generally more energy-efficient and produce fewer emissions than traditional wood-burning fireplaces.
Q: How can I improve the energy efficiency of my fireplace?
A: To improve energy efficiency, consider using a high-efficiency model, maintaining proper clearances, and utilizing zone heating.
Q: Are there energy efficiency certifications for fireplaces?
A: Yes, some Stellar Fireplaces models may be certified by organizations like ENERGY STAR for energy efficiency. Check product specifications for certifications.
Installation and Maintenance
Q: Do I need a chimney for an electric fireplace?
A: No, electric fireplaces do not require a chimney or venting. They are typically plugged into an electrical outlet.
Q: How often should I clean my wood-burning fireplace chimney?
A: Clean your wood-burning fireplace chimney at least once a year to remove creosote buildup and ensure safety.
Q: Can I install a fireplace myself, or should I hire a professional?
A: Installation complexity varies by type and model. Gas and wood-burning fireplaces often require professional installation due to safety and code compliance. Electric fireplaces are generally easier for DIY installation.
Q: Do I need permits for fireplace installation?
A: Permit requirements vary by location. Check with your local building department to determine if permits are needed for fireplace installation.
Q: What are some common maintenance tasks for fireplaces?
A: Maintenance tasks include cleaning the glass, inspecting and cleaning chimneys, and checking for proper venting.
Q: Can I use an existing chimney with a new fireplace?
A: In some cases, you can use an existing chimney with a new fireplace, but it must meet the requirements and be properly retrofitted.
Heating and Usage
Q: Are electric fireplaces suitable for heating large spaces?
A: Electric fireplaces are often used for supplemental heating in smaller to medium-sized spaces. Their heating capacity varies depending on the model.
Q: What is zone heating, and how does it work with fireplaces?
A: Zone heating involves heating specific areas of your home with a fireplace or space heater instead of relying on central heating for the entire house. It can be cost-effective and energy-efficient.
Q: Can I use a fireplace as the primary heating source for my home?
A: Depending on the type and size of the fireplace and the climate in your area, a fireplace can be used as a primary or supplemental heating source. Consult with a professional for guidance.
Safety and Environmental Concerns
Q: Are there safety precautions I should take when using a fireplace?
A: Yes, follow safety precautions, including installing smoke and carbon monoxide detectors, maintaining clearances, and using proper fuels.
Q: Are there environmental concerns associated with using fireplaces?
A: Depending on the type and use of the fireplace, there can be environmental impacts, such as emissions and fuel consumption. Proper maintenance and efficient models can minimize these impacts.
Customization and Budgeting
Q: How do I choose the right fireplace for my home?
A: Consider factors such as your heating needs, budget, fuel type, and design preferences when choosing a fireplace.
Q: Are there options for customizing the appearance of my fireplace?
A: Yes, many Stellar Fireplaces offer customization options, including mantels, surrounds, and decorative finishes.
Q: What should I consider when budgeting for a fireplace project?
A: Consider the type of fireplace, installation costs, ongoing fuel and maintenance expenses, and any additional features or accessories.