Table of Contents
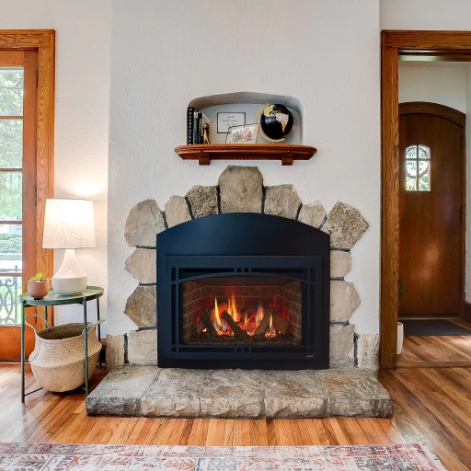
Fireplaces are a cozy addition to any home, but can you get a fireplace too hot?
We’ll explore the risks of overheating your fireplace, including fire hazards, carbon monoxide poisoning, and damage to the fireplace and surrounding areas.
We’ll also discuss what causes a fireplace to get too hot and provide tips on how to prevent it.
Learn what to do if your fireplace gets too hot and whether you can use your fireplace too much.
Can You Get a Fireplace Too Hot?
It is possible to get a fireplace too hot if proper control and monitoring measures are not in place to prevent overheating and associated risks.
An overly hot fireplace can pose various safety challenges.
For instance, it can ignite nearby flammable objects or cause structural damage to the chimney or surrounding walls.
Monitoring the temperature of the fireplace is crucial to ensure that it remains within a safe range.
Implementing safety measures like using a fireplace screen, maintaining proper ventilation, and installing temperature sensors can help mitigate these risks.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the fireplace and chimney are essential to prevent overheating and address any potential issues promptly.
What are the Risks of Getting a Fireplace Too Hot?
Getting a fireplace too hot poses significant risks such as fire hazards, carbon monoxide poisoning, and damage to both the fireplace and surrounding areas.
A major concern with overheating a fireplace is the increased likelihood of fire hazards.
When a fireplace gets excessively hot, it can ignite nearby flammable materials, leading to a potential house fire.
The intense heat can cause structural damage to the fireplace itself, such as cracks in the bricks or mortar, which could compromise its integrity.
Overheating can elevate the levels of carbon monoxide emitted by the fireplace, putting inhabitants at risk of carbon monoxide poisoning, a silent yet deadly threat.
Therefore, it is crucial to practice safety measures like using a fireplace screen, monitoring the temperature, and ensuring proper ventilation to prevent these hazards.
Fire Hazards
One of the primary risks of having a fireplace too hot is the increased potential for fire hazards due to the overheating of flammable materials.
Excessively hot fireplaces can quickly transform from cozy hearths to dangerous sources of ignition.
When the surrounding materials, such as curtains, furniture, or wooden mantels, are exposed to extreme heat, the risk of combustion significantly rises.
This heightened temperature can cause these items to catch fire unexpectedly, leading to uncontrolled flames.
To prevent such incidents, it is crucial to monitor the fireplace’s temperature consistently and adhere to safety guidelines.
These include proper ventilation, regular chimney inspections, and using appropriate fire tools.
By maintaining caution and implementing preventive measures, homeowners can reduce the likelihood of fire-related accidents.
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
When a fireplace becomes too hot, there is a heightened risk of carbon monoxide poisoning, emphasizing the importance of safety features to detect and prevent such dangers.
Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas produced when fuels like wood, gas, or oil burn incompletely.
Exposure to this gas can lead to symptoms like headaches, dizziness, nausea, and even death in severe cases.
That’s why having carbon monoxide detectors installed near fireplaces is crucial.
These detectors can quickly identify elevated levels of the gas and alert occupants to evacuate the area.
They serve as a critical line of defense, providing early warnings that can save lives and prevent tragic outcomes.
Damage to Fireplace and Surrounding Areas
An excessively hot fireplace can result in damage not only to the fireplace itself but also to the surrounding areas.
This underscores the importance of following safety instructions to prevent such scenarios.
When a fireplace overheats, it poses various risks including structural damage to the chimney, walls, and flooring.
The intense heat generated can weaken the materials, leading to cracks, warping, or even fires.
Hot fireplaces raise safety concerns such as the risk of nearby objects catching fire or individuals getting burnt.
It’s crucial to exercise caution, ensuring proper ventilation and using suitable firewood to regulate the temperature within safe limits.
By adhering to safety guidelines and undertaking preventive measures, homeowners can mitigate the potential dangers associated with overheating fireplaces.
What Causes a Fireplace to Get Too Hot?
Several factors can cause a fireplace to get too hot, including poor airflow, the use of inappropriate fuel, and lack of proper maintenance.
Inadequate airflow circulation is a common issue that can lead to overheating in fireplaces.
When the airflow is restricted, heat cannot escape efficiently, causing the temperature inside the fireplace to rise rapidly.
Using incorrect fuel choices, such as burning materials that produce excessive heat, can further exacerbate the problem.
Insufficient maintenance practices, like not cleaning the chimney regularly or neglecting to inspect the fireplace components, can also contribute to overheating.
These factors combined pose several risks, such as an increased chance of a fire outbreak, damage to the fireplace structure, and potential harm to individuals nearby.
Therefore, it is crucial to prioritize safety measures, such as installing proper ventilation systems, using appropriate fuel sources, and scheduling routine maintenance checks to prevent dangerous situations.
Poor Airflow
Insufficient airflow around the fireplace can contribute to overheating issues, posing safety concerns and risks associated with excessive heat build-up.
When air is not properly circulated near the fireplace, the heat generated from the burning fire has limited outlets to escape.
This leads to a buildup of intense heat in the immediate vicinity.
This situation can result in various safety hazards, such as the risk of nearby objects catching fire, walls becoming overly heated, and even the potential for the chimney and surrounding structural elements to become dangerously hot.
Effective ventilation and airflow management play a crucial role in dissipating this excess heat, ensuring that the fireplace operates safely and efficiently.
Using Inappropriate Fuel
The choice of inappropriate fuel for a fireplace can result in increased heat production, posing risks that necessitate safety precautions to prevent overheating.
Using the wrong type of fuel, such as combustibles like gasoline, can lead to a rapid escalation in temperatures within the fireplace.
This increase in heat not only raises the risk of overheating the surrounding area but can also lead to potential fire hazards.
It is crucial to opt for suitable fuel options like seasoned wood or manufactured fire logs, as they burn more steadily and produce controlled heat levels.
Implementing safety measures such as installing a spark guard and monitoring the temperature regularly can help regulate the fire’s intensity and ensure a safe fireplace experience.
Improper Maintenance
Neglecting proper maintenance practices for a fireplace can result in overheating risks, emphasizing the need for safety controls to prevent dangerous heating levels.
This can lead to a variety of safety hazards, including the risk of chimney fires and carbon monoxide poisoning.
By regularly inspecting and cleaning the fireplace and chimney, homeowners can ensure proper airflow and prevent blockages that could contribute to excessive heat buildup.
In addition, installing a temperature sensor or heat regulator can help monitor and control the temperature, reducing the chances of overheating.
Proper maintenance not only ensures the efficient operation of the fireplace but also plays a crucial role in safeguarding the home and its occupants from potential dangers.
How to Prevent a Fireplace from Getting Too Hot?
Preventing a fireplace from getting too hot involves regular maintenance and inspections, proper use of the fireplace, and monitoring the temperature to ensure safety and prevent damage.
- Regular maintenance checks are crucial to ensure that the fireplace is in proper working condition and to identify any potential issues that could lead to overheating.
- Maintaining a clean chimney and flue, checking for cracks or leaks in the fireplace structure, and ensuring proper ventilation are all key aspects of maintenance.
- Correctly operating the fireplace by using the appropriate fuel types, following manufacturer guidelines, and not overloading the firebox can help prevent excessive heat build-up.
It is also advisable to install temperature monitoring tools such as heat sensors or thermometers to continuously track the temperature levels.
Promptly addressing any spikes that could pose a risk is essential.
By combining these preventive measures and staying vigilant, homeowners can enjoy their fireplace safely and efficiently without the worry of overheating-related hazards.
Regular Maintenance and Inspections
Regular maintenance and thorough inspections are key to preventing fireplaces from getting too hot, aligning with safety guidelines to ensure optimal performance and safety.
By adhering to a routine maintenance schedule, homeowners can avoid the risks of overheating and potential fire hazards associated with neglected fireplaces.
Conducting detailed inspections allows for the early identification of any issues that may compromise the safe operation of the fireplace.
It is crucial to check for blockages in the flue, ensure proper ventilation, and monitor the temperature to prevent excessive heat build-up.
Following safety guidelines when cleaning and maintaining the fireplace, such as using the appropriate tools and materials, further enhances the overall safety of the heating system.
Proper Use of Fireplace
Correct and proper usage of the fireplace is essential in preventing it from getting too hot, adhering to safety recommendations for avoiding overheating incidents.
Fireplaces are not only a source of warmth and ambiance but also potential hazards if not used correctly.
To maintain a controlled temperature environment and minimize risks, it is crucial to follow best practices.
One important tip is to avoid burning materials that produce excessive heat or sparks, as this can lead to a dangerous situation.
Always ensure that the damper is open when the fireplace is in use to allow proper ventilation and prevent the buildup of heat.
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and inspecting the chimney, is also key to safe fireplace operation.
Monitoring Temperature
Monitoring the temperature of the fireplace regularly is crucial in preventing overheating, aligning with safety standards to ensure safe and controlled heating levels.
By keeping a close eye on the temperature, household members can avoid potential fire hazards and ensure efficient heat distribution throughout the living space.
Safety regulations emphasize the need for maintaining optimal heat levels to prevent accidents.
To assist in monitoring fireplace temperatures effectively, various tools such as infrared thermometers, digital temperature gauges, and smart temperature sensors are available.
These tools provide accurate readings and allow users to adjust heating settings promptly, promoting a safe and comfortable environment.
Implementing routine maintenance checks and cleaning procedures on the fireplace can further enhance safety compliance and prevent overheating issues.
What to Do if Your Fireplace Gets Too Hot?
If your fireplace gets too hot, immediate actions such as opening windows and doors, turning off the fireplace, and seeking professional help are vital to ensure safety and prevent potential hazards.
Opening ventilation points can help release excess heat and smoke efficiently, reducing the risk of fire spreading to other areas of the house.
Shutting off the fireplace allows it to cool down gradually and minimizes the chances of further overheating.
Contacting professionals, such as certified chimney sweeps or fireplace technicians, is crucial to assess the situation thoroughly.
They can address any underlying issues that may have caused the overheating.
Prompt actions are essential in managing overheated fireplaces to prevent property damage, injuries, or even potential fatalities.
Open Windows and Doors
Opening windows and doors when a fireplace gets too hot can help dissipate excess heat, providing immediate safety relief and lowering the temperature indoors.
This simple action allows for improved air circulation, preventing the buildup of excessive heat in a confined space.
By creating a cross breeze, fresh air can flow in while hot air is pushed out, effectively cooling down the environment.
It is crucial to maintain proper ventilation around the fireplace to prevent overheating and ensure a safe indoor atmosphere.
Installing a heat-resistant barrier around the fireplace can help in directing the heat appropriately and minimize potential hazards.
Turn Off the Fireplace
In cases of overheating, turning off the fireplace immediately is a critical safety instruction to prevent further heat buildup and potential risks of fire or damage.
- To safely turn off the fireplace, start by locating the main power switch or control panel of the unit.
- Once identified, switch off the power source to halt the fuel supply.
- Next, close the damper or air intake vents to restrict oxygen flow and suppress the flames.
- Avoid using water to extinguish the fire, as it can lead to steam and thermal shock.
- If the situation persists or worsens, evacuate the area immediately and contact emergency services for assistance.
Call for Professional Help
Seeking professional assistance when a fireplace overheats is crucial to address potential risks effectively and ensure safety protocols are followed to mitigate hazards.
Professionals have the necessary expertise and training to evaluate the root cause of overheating, which can range from issues with the chimney to problems with the airflow.
By entrusting the evaluation and resolution to experts, homeowners can have peace of mind knowing that their fireplace is being handled safely and effectively.
These professionals can also provide valuable insights on preventive maintenance measures to avoid future overheating incidents.
Ultimately, this safeguards the home and its occupants from the dangers associated with fireplace malfunctions.
Can You Use a Fireplace Too Much?
Excessive use of a fireplace can raise safety concerns related to air quality, potential damage to the fireplace structure, and other safety hazards that necessitate precautionary measures.
When a fireplace is used excessively, the air quality within a home can be compromised due to the release of harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide.
Prolonged exposure to such pollutants can lead to respiratory issues and other health problems.
The continuous use of a fireplace can pose a risk of overheating the structure, potentially causing damage to the chimney or surrounding walls.
It is crucial for individuals to implement precautionary measures to regulate fireplace usage.
This includes proper ventilation, regular maintenance checks, and adhering to recommended burning guidelines to ensure safe and controlled heating practices.
Effects on Air Quality
Using a fireplace too much can have adverse effects on indoor air quality, raising safety concerns related to ventilation, particulate matter, and overall respiratory health.
Excessive usage of a fireplace can lead to a buildup of harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen dioxide in the indoor environment.
This poses serious risks to respiratory health.
Poorly ventilated spaces can trap these pollutants, increasing the concentration of harmful particles in the air.
Particulate emissions from burning wood or other fuels can also contribute to indoor air pollution, aggravating conditions like asthma and allergies.
To mitigate these effects, it’s crucial to ensure proper ventilation and regular maintenance of the fireplace and chimney.
Damage to Fireplace
Overusing a fireplace can result in structural damage over time, highlighting safety concerns related to maintenance requirements and the longevity of the fireplace.
To prevent such risks, it is crucial to follow proper maintenance practices and set limits on usage.
Regularly inspecting the fireplace for any signs of wear and tear, such as cracks in the chimney or deterioration of the bricks, can help identify potential issues early on.
Ensuring that the fireplace is cleaned regularly to remove any creosote buildup, a common cause of chimney fires, is essential.
Limiting the amount of wood or other fuel used per fire can also help prevent excessive heat that can lead to structural damage.
Remember to always use a fireplace screen to contain embers and sparks, reducing the risk of fires outside the fireplace area.
Safety Concerns
Excessive fireplace usage raises safety concerns regarding fire risks, carbon monoxide exposure, and potential hazards that necessitate adherence to safety precautions for risk mitigation.
- Fireplaces, while providing warmth and ambiance, can pose serious dangers if not used properly.
- One major risk is the possibility of a fire breaking out due to creosote build-up in the chimney or improper maintenance of the fireplace.
- The release of carbon monoxide from burning wood can lead to poisoning if the area is not adequately ventilated.
To ensure safe usage, it is crucial to have regular chimney inspections, use proper safety tools like screens and glass doors, and never leave a fire unattended.
Adequate ventilation and proper fuel selection are also key factors in maintaining a safe environment when enjoying a cozy fire at home.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can a fireplace get too hot?
Yes, a fireplace can get too hot if there are no proper control and monitoring measures in place to prevent overheating.
2. What risks are associated with an overheated fireplace?
Risks include fire hazards, carbon monoxide poisoning, structural damage to the fireplace and surrounding areas, and potential personal injury.
3. What causes a fireplace to overheat?
Causes include poor airflow, inappropriate fuel use, lack of maintenance, or blockages in the chimney or flue.
4. How can I prevent my fireplace from getting too hot?
Prevent overheating by ensuring regular maintenance, using appropriate fuel, monitoring temperature, and adhering to safety guidelines.
5. What should I do if my fireplace gets too hot?
If your fireplace gets too hot, open windows and doors to ventilate, turn off the fireplace, and seek professional help if needed.
6. How often should I inspect my fireplace?
Inspect your fireplace at least once a year to check for blockages, structural issues, and to ensure proper ventilation.
7. Can I use any type of wood in my fireplace?
No, you should use only seasoned wood or manufactured logs, as other materials can produce excessive heat and potentially lead to unsafe conditions.
8. What are the signs of carbon monoxide poisoning?
Signs include headaches, dizziness, nausea, confusion, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness. It’s vital to have carbon monoxide detectors near your fireplace.
9. Does excessive fireplace use affect air quality?
Yes, excessive use can lead to poor indoor air quality due to the release of harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide and particulate matter.
10. How can I ensure proper ventilation for my fireplace?
Ensure proper ventilation by keeping the damper open during use, regularly checking for blockages, and using fans to improve airflow in the room.
Latest Articles

What Is An NG (Natural Gas) Indicator And Why You Need It For Your Fireplace
Table of Contents1 Understanding Natural Gas Fireplaces2 What is an NG Indicator?3 Importance of NG Indicators for Safety4 Types of NG Indicators5 Installation and Maintenance of NG Indicators6 Signs of a Faulty NG Indicator7 Frequently Asked Questions Natural gas fireplaces are a favored option among numerous homeowners due to their convenience and effectiveness. But, what is an NG (Natural Gas) indicator and why you need it for your fireplace? It is imperative to comprehend how they function and the significance of having an NG (Natural Gas) indicator for safety purposes. This article delves into the definition and significance of NG indicators. We will discuss the potential hazards associated with the absence of one and the various types of indicators accessible. Also, we will discuss installation and maintenance recommendations, and methods to recognize and rectify issues with malfunctioning indicators. Stay well-informed and ensure the safety of your home by referring to this exhaustive guide. Understanding Natural Gas Fireplaces Natural gas fireplaces serve as an efficient and convenient heating option for numerous households. They utilize natural gas as a fuel source to deliver consistent warmth and ambiance. How They Work and Why They Need NG Indicators The operation of natural gas fireplaces involves igniting natural gas to generate heat. This process requires diligent monitoring to ensure both safety and efficiency, a task facilitated by the use of NG indicators. NG indicators play a critical role in detecting potential gas leaks. They enable residents to promptly address and mitigate any associated hazards. Through continuous monitoring of gas levels and providing timely warnings and alerts, NG indicators uphold a secure indoor environment. It is imperative to ensure that these indicators function properly to facilitate the effective operation of natural gas fireplaces. This helps mitigate the inherent risks linked to gas leaks. What is an NG Indicator? An NG indicator is a specialized device equipped with advanced sensors and technology. It is specifically designed to detect natural gas leaks and monitor gas pressure in appliances, such as fireplaces. Definition and Purpose The NG indicator functions as a detector that monitors gas appliances for potential leaks. It provides essential functionality to ensure safety in households utilizing natural gas. These detectors play a crucial role in protecting residences by notifying occupants of dangerous gas leaks long before they escalate into perilous situations. Through continuous monitoring of gas levels in the vicinity, NG indicators offer an additional layer of protection. This is particularly important in properties that rely on gas-operated fireplaces or stoves. These devices not only help avert potential disasters but also enhance the overall peace of mind of homeowners. They assure them that their living spaces are equipped with reliable safety features. Importance of NG Indicators for Safety Natural gas indicators are essential for maintaining safety in households equipped with natural gas appliances. These devices serve as a proactive measure to promptly detect gas leaks. This offers homeowners a sense of security and assurance. Potential Dangers of Not Having an NG Indicator The absence of an NG indicator in residences equipped with natural gas appliances can pose significant hazards. This includes the risk of undetected gas leaks , carbon monoxide poisoning , and pilot outages that may lead to dangerous situations. These potential risks can profoundly impact indoor air quality. They directly influence the health and safety of individuals residing in the household. Undetected gas leaks can go unnoticed, gradually permeating the air and creating a potentially explosive environment. Insufficient ventilation from undetected exposure to carbon monoxide can lead to serious health complications. These range from mild symptoms such as dizziness to fatal poisoning. Without proper monitoring from an NG indicator, families are left susceptible to these concealed threats. This underscores the critical importance of implementing proactive measures to mitigate such risks. Types of NG Indicators Indicators for Natural Gas (NG) are available in diverse types. Each presents distinct detection capabilities tailored to specific requirements, encompassing both manual and automated alternatives. Manual vs. Automatic Indicators Manual NG indicators require user intervention for monitoring gas levels and identifying leaks. On the other hand, automatic indicators employ sophisticated technology to deliver continuous, real-time monitoring. This heightened efficiency and oversight enhance safety protocols. Conventional manual indicators rely on individuals to physically inspect and evaluate gas levels periodically. This renders them more susceptible to human errors. Conversely, automatic indicators feature sensors capable of promptly detecting even the most minute fluctuations in gas levels. This establishes a more dependable and precise monitoring mechanism. Automatic indicators can activate alerts and shut-off systems upon detecting a leak. This ensures immediate action to avert potential hazards. This advanced technology enhances safety protocols and instills a sense of command and assurance among users. Installation and Maintenance of NG Indicators The reliable and accurate performance of NG indicators necessitates proper installation and consistent maintenance. This often entails professional installation and adherence to recommended service guidelines. Proper Installation and Regular Maintenance Tips The proper installation of NG indicators involves adhering to the specifications in the user manual. Maintenance protocols entail strict adherence to a predetermined maintenance schedule to ensure sustained operational efficiency. During the installation phase, it is imperative to verify that the NG indicators are securely affixed in the designated location as stipulated by the manufacturer. Crucial steps include confirming power source compatibility and ensuring proper grounding of the device to optimize performance. Calibration of the indicator must be executed meticulously to ensure precise readings. Regarding maintenance, essential practices include regular inspection for signs of wear, thorough cleaning of the indicator components, and routine functionality tests. By allocating time to a consistent maintenance regimen, the NG indicator can operate with optimal efficiency over an extended duration. Signs of a Faulty NG Indicator Recognizing indicators of a malfunctioning NG indicator is essential for upholding safety and performance standards. Inaccuracies and detection issues can undermine the efficacy of these devices. Identifying and Addressing Issues The process of identifying and addressing issues related to NG (natural gas) indicators requires a systematic troubleshooting approach. This ensures their optimal performance

What You Need To Know About Gas Log Set Safety And Installation Considerations
Table of Contents1 Understanding Gas Log Sets2 Safety Considerations for Gas Log Sets3 Installation Guidelines for Gas Log Sets4 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Gas Log Sets5 Frequently Asked Questions Gas log sets are a favored option among homeowners seeking to enjoy the comfort and atmosphere of a conventional fireplace without the inconvenience of wood. This article tells you what you need to know about gas log set safety and installation considerations. Before incorporating one into your residence, it is imperative to understand the safety considerations associated with their use. This discussion delves into the potential hazards linked with gas log sets. It presents crucial precautions to uphold the safety of your home. Also, it outlines proper installation procedures and offers insight into common errors to avoid. Finally, it provides advice on maintenance and troubleshooting. Gain comprehensive knowledge on gas log set safety and installation considerations. Understanding Gas Log Sets Comprehending gas log sets is essential for individuals seeking to elevate their fireplace experience, and for gas lag set safety and installation. These heating appliances can operate on either natural gas or propane. In addition, they are available in a range of styles, including vented, ventless, and vent-free options. They provide an array of benefits and customization opportunities through various fireplace accessories. What are Gas Log Sets? Gas log sets are meticulously crafted artificial logs. They are designed to imitate the appearance and functionality of authentic wood logs within fireplaces. These gas log sets typically consist of ceramic or refractory concrete logs that have been skillfully molded and painted. This allows them to replicate the natural grain and texture of real wood. The logs are arranged in various configurations within the fireplace. They establish a realistic and welcoming ambiance. In addition to the logs, gas log sets often include fireplace accessories such as glowing embers. Accessories also include decorative stones, and even pine cones to enhance the overall aesthetic appeal. Homeowners can select from an array of placement options. These include traditional wood stack, cascading driftwood, or a contemporary geometric arrangement. Homeowners can align their preferred style and design preferences. Safety Considerations for Gas Log Sets Safety considerations for gas log sets are of utmost importance to guarantee a secure and pleasant fireplace experience. It is essential to address potential hazards such as carbon monoxide exposure, gas leaks, and fire safety to maintain a safe environment for homeowners. Potential Hazards and Precautions Gas log sets come with potential hazards that must be taken seriously, including the risks of gas leaks, carbon monoxide poisoning, and fire incidents. It is imperative to establish and adhere to rigorous safety measures to ensure the well-being of individuals and properties involved in the use of gas log sets. Gas leaks represent a significant hazard when utilizing gas log sets. They can result in the accumulation of combustible gas within the premises, heightening the possibility of explosions or fires. Carbon monoxide, an insidious gas generated during incomplete combustion, poses a grave threat due to its colorless and odorless nature, making it undetectable without proper monitoring. To address these risks effectively, it is vital to install carbon monoxide detectors and gas leak sensors in the vicinity of the gas logs. Routine maintenance checks on the gas log system, including cleaning and inspection procedures, are critical to ensure safe operations and the prompt identification of potential issues. In case of a gas leak or suspected presence of carbon monoxide, immediate evacuation of the affected area is paramount, followed by prompt contact with emergency services. Recognizing the distinct odor of rotten eggs associated with natural gas can serve as an early warning sign, prompting swift actions to avert any potential accidents. Installation Guidelines for Gas Log Sets The installation of a gas log set necessitates meticulous planning and strict adherence to specific guidelines. This includes verifying a secure gas connection, ensuring proper gas lines are in place, and complying with local building codes. Often, the complexity of these requirements may require the expertise of a certified technician. Proper Installation Techniques The appropriate installation procedures for gas log sets involve the secure connection of gas lines, meticulous adherence to installation manuals, and strict compliance with local building codes. It is imperative to prioritize the guarantee of secure gas connections to avert leaks and potential safety hazards. During the installation of gas log sets, utilizing suitable sealants and fittings is essential to establish a tightly sealed connection. The correct installation of gas lines is critical for both the safety and operational efficacy of the gas log set. Reference to the installation manual is highly advisable for detailed, step-by-step guidance to prevent inaccuracies and ensure the successful establishment of the gas log set. Consistently adhering to building codes and regulations upholds safety standards. Seeking guidance and confirmation from a certified technician before and after installation can offer invaluable support and assurance throughout the process. Common Installation Mistakes to Avoid It is imperative to avoid common installation errors to ensure the secure and effective operation of gas log sets. This includes verifying proper gas connections and compliance with building codes. Improper gas connections can result in leaks and potential hazards, underscoring the importance of verifying the tightness and correct alignment of all fittings. Failure to adhere to building codes can lead to structural complications, penalties for non-compliance, or even safety concerns. To prevent these oversights, it is advised to consult the manufacturer’s installation guidelines and strictly adhere to local regulations. Engaging a certified technician for the installation of gas log sets guarantees that the procedure is carried out accurately and securely. This provides assurance that the system is functioning as intended. Maintaining and Troubleshooting Gas Log Sets Regular maintenance and troubleshooting of gas log sets are imperative to uphold their optimal performance and safety. This includes thorough examination of the pilot light, pilot assembly, and other gas appliances to preserve heating efficiency and promptly resolve any arising issues. Tips for Maintenance and Repair Ensuring the proper maintenance of your gas log set necessitates conducting

Key Considerations For Using Compressed Liquid Propane In Fireplace Installation
Table of Contents1 What is Compressed Liquid Propane?2 Benefits of Using Compressed Liquid Propane in Fireplaces3 Safety Precautions for Installing Compressed Liquid Propane Fireplaces4 Installation Process for Compressed Liquid Propane Fireplaces5 Maintenance and Care for Compressed Liquid Propane Fireplaces6 Alternative Fuel Options for Fireplaces7 Frequently Asked Questions If you are contemplating the use of compressed liquid propane in your fireplace installation, this discussion will delve into the advantages of adopting this alternative fuel option. These benefits include enhanced efficiency, cost savings, and important safety precautions to consider. Furthermore, a detailed step-by-step guide on the installation process will be provided, along with recommendations for maintenance and care. A comparison of various fuel options for fireplaces will also be conducted to assist you in making an informed decision. We encourage you to stay engaged to gain insights into optimizing your fireplace’s capabilities with compressed liquid propane. What is Compressed Liquid Propane? Compressed Liquid Propane is a versatile energy source contained in a high-pressure propane tank. It finds extensive utility in both residential and commercial settings, prominently including fireplaces. Recognized for its convenience and efficiency, Compressed Liquid Propane emerges as a favored option for heating residential spaces and facilitating culinary pursuits across various environments. Additionally, it serves as a viable fuel substitute in vehicular contexts, portable cooktops, and outdoor grilling scenarios due to its propensity for clean combustion. The attribute of portability, coupled with ease of storage, positions Compressed Liquid Propane as an optimal energy source for individuals residing off the conventional grid. It is also great for engaging in outdoor activities such as camping and recreational vehicle (RV) travel. Moreover, the high energy density inherent to Compressed Liquid Propane renders it a dependable choice for sustaining generators during instances of power disruptions. Benefits of Using Compressed Liquid Propane in Fireplaces Utilizing Compressed Liquid Propane for fireplace installation presents several benefits. These include enhanced fuel efficiency, convenience, cost-effectiveness, and a favorable environmental footprint. These attributes render it a recommended option for heating solutions, applicable to both on-grid and off-grid settings. Efficiency and Cost Savings The utilization of Compressed Liquid Propane in fireplaces offers significant advantages, notably in terms of high fuel efficiency and cost-effectiveness. These attributes are underscored by the exceptional BTU rating and overall heating efficiency of Compressed Liquid Propane. The elevated fuel efficiency exhibited by Compressed Liquid Propane fireplaces necessitates less fuel to generate the same level of heat compared to traditional wood-burning fireplaces or electric heating systems. Consequently, homeowners can realize cost savings on their heating expenditures over an extended period. Moreover, the clean-burning characteristics of propane minimize maintenance costs linked to soot and ash cleanup. This further enhances the cost-effectiveness of employing propane fireplaces. Safety Precautions for Installing Compressed Liquid Propane Fireplaces Ensuring safety is of utmost importance during the installation of Compressed Liquid Propane fireplaces. This requires strict adherence to safety regulations, meticulous attention to proper ventilation requirements, careful control of ignition sources, and the incorporation of carbon monoxide and gas leak detection systems. Important Safety Measures Essential safety protocols for the installation of Compressed Liquid Propane fireplaces encompass adherence to fire safety regulations. Engaging in professional assessments and employing sophisticated gas leak and carbon monoxide detection mechanisms is crucial. Professional evaluations play a critical role in identifying any prospective hazards or irregularities within the fireplace infrastructure. These assessments are vital in ensuring the operational integrity of all components and compliance with safety protocols. Routine inspections serve to forestall potential fire incidents, gas discharges, or carbon monoxide emissions that could pose significant threats to both the property and individuals in the vicinity. The utilization of advanced gas leak and carbon monoxide detection systems serves as an additional safeguard by promptly notifying occupants of any elevated levels of these hazardous gases. Installation Process for Compressed Liquid Propane Fireplaces The installation procedure for Compressed Liquid Propane fireplaces encompasses several critical steps. These include: Adhering to installation guidelines Correctly positioning the propane tank Ensuring precise gas line installation Optimizing heat output Monitoring pressure regulation Establishing the pilot light Step-by-Step Guide The installation process of Compressed Liquid Propane fireplaces involves a systematic approach. This begins with the construction of the firebox, followed by the installation of the gas control valve, setup of the ignition system, design of the flue, and verification of a suitable combustion air supply. The construction of the firebox assumes critical importance as it serves as the foundation of the fireplace structure. It securely holds the combustible materials in place. Subsequently, the gas control valve plays a key role in managing the propane flow, guaranteeing safe and efficient operation. The installation of the ignition system facilitates convenient and reliable fire initiation. Designing the flue is a necessary step to direct exhaust gases outside, thus preventing their accumulation indoors. Moreover, ensuring a proper combustion air supply is essential to sustain optimal burning conditions and enhance fuel consumption efficiency. Each component contributes significantly to the functionality and safety of the fireplace installation process. This underscores the importance of meticulous attention to detail and adherence to established protocols. Maintenance and Care for Compressed Liquid Propane Fireplaces Consistent maintenance and attention to Compressed Liquid Propane fireplaces are imperative to guarantee their optimal functionality. This includes adherence to prescribed maintenance protocols, regular chimney upkeep, prevention of soot accumulation, and scheduling of routine propane deliveries and professional inspections. Tips for Keeping Your Fireplace in Good Condition For the maintenance of your Compressed Liquid Propane fireplace, it is essential to conduct regular checks on ignition sources. Monitor flame appearance, clean the gas burner and pilot assembly, and verify the correct operation of the safety shut-off valve. The inspection of ignition sources requires a detailed examination of the electronic igniter. This helps identify any signs of damage or corrosion and ensures proper sparking upon activation. Monitoring flame appearance involves observing a consistent blue flame with minimal flickering, which signifies efficient combustion. Cleaning the gas burner and pilot assembly can be performed using a soft brush or compressed air to eliminate any dirt or debris that may